low end tidal co2 during cpr
Web Amplitude Spectrum Area AMSA values during ventricular fibrillation VF correlate with myocardial energy stores and predict defibrillation successBy contrast end tidal CO 2. Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient.

Sar Helicopter Paramedic Practice Etco2 Measuring To Assist With Cpr Attempts Journal Of Paramedic Practice
Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient.

. However there was no evidence in the medical record staff. Evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions is accomplished in the. Web End-tidal carbon dioxide CO 2 monitoring is a safe and effective noninvasive indicator of cardiac output CO during CPR.
Web A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest.
On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing airway obstruction or. The major determinant of CO 2 excretion is its rate of delivery from the peripheral production sites to the lungs. During cardiac arrest CO 2 continues to be generated throughout the body.
Web End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status. Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are.
Web During CPR end tidal CO2 ETCO2 is a relative indicator of cardiac output and should be used if possible. Is inversely indicated by the amount of light that passes through the sensor. Web What should end-tidal be during CPR.
Web End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 as measured by waveform capnography is considered a physiologic measure of cardiac output in low-flow states. Web Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. Web End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a noninvasive technique which measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled.
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement in and out of the lungs ventilation CO2. Web Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed. Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al.
High CO2 levels are indicated by low infrared and low CO2 levels result in. Web End-tidal carbon dioxide. Web 2 USES DURING CPR 7 CONFIRM ADEQUACY OF CHEST COMPRESSIONS.
Web In this analysis the authors found that the average EtCO 2 level of 25 mmHg in patients with ROSC is notably higher than the threshold of 10 to 15 mmHg.
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationwhen Is Capnography Useful In The Ed Part Ii Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Concentration During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Nejm

End Tidal Co2 In Cardiac Arrest Nuem Blog

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Error In Capnography Infographic Emcrit Project

Association Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Levels During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation With Survival In A Large Paediatric Cohort Sciencedirect
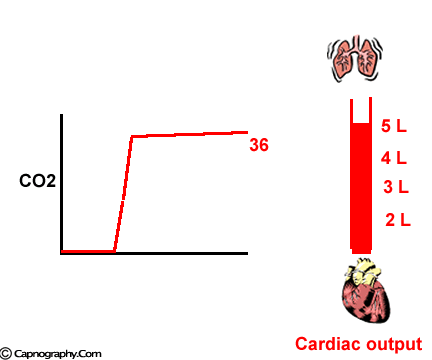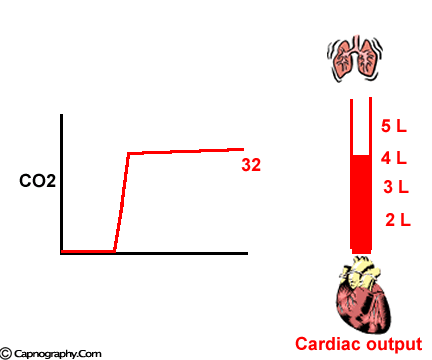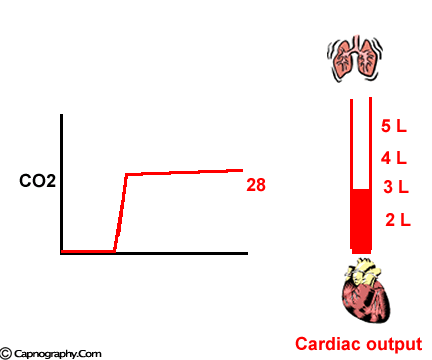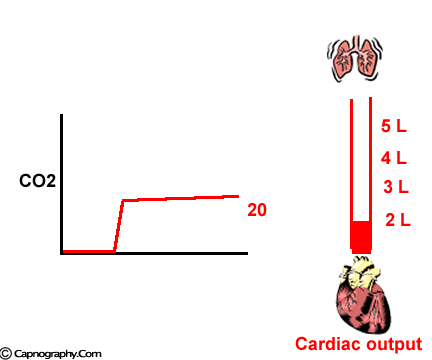
Petco2 And Cardiac Output Capnography

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Concentration During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Nejm

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

End Tidal Co2 Monitoring Noninvasive Respiratory Monitoring For The

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

End Tidal Co2 In Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Etco2 In Cpr
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Concentration During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Nejm

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
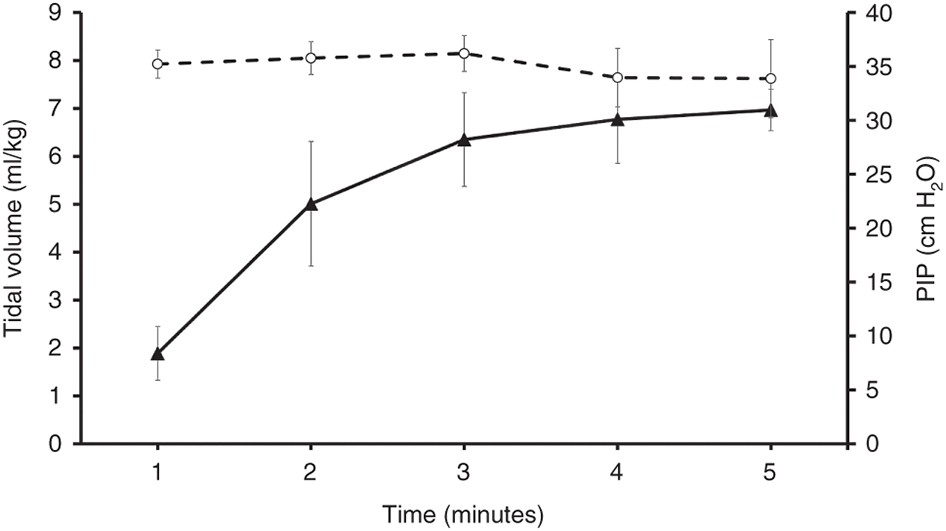
Continuous Capnography Monitoring During Resuscitation In A Transitional Large Mammalian Model Of Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Pediatric Research

Capnography For Cpr Nonin Pdf Catalogs Technical Documentation